Help
Overview
The kmerDB web interface (Fig. 1) presents the following options:
- Browse organisms: Browse the database by organism genome or proteome
- Help: this help page
- About: Database information
- Quick Search: Perform a quick, keyword-based search on the database's contents, either Genomes or Proteomes.
- Advanced Search: perform a more refined search with extra settings.
- Login: Access to restricted content (see below).
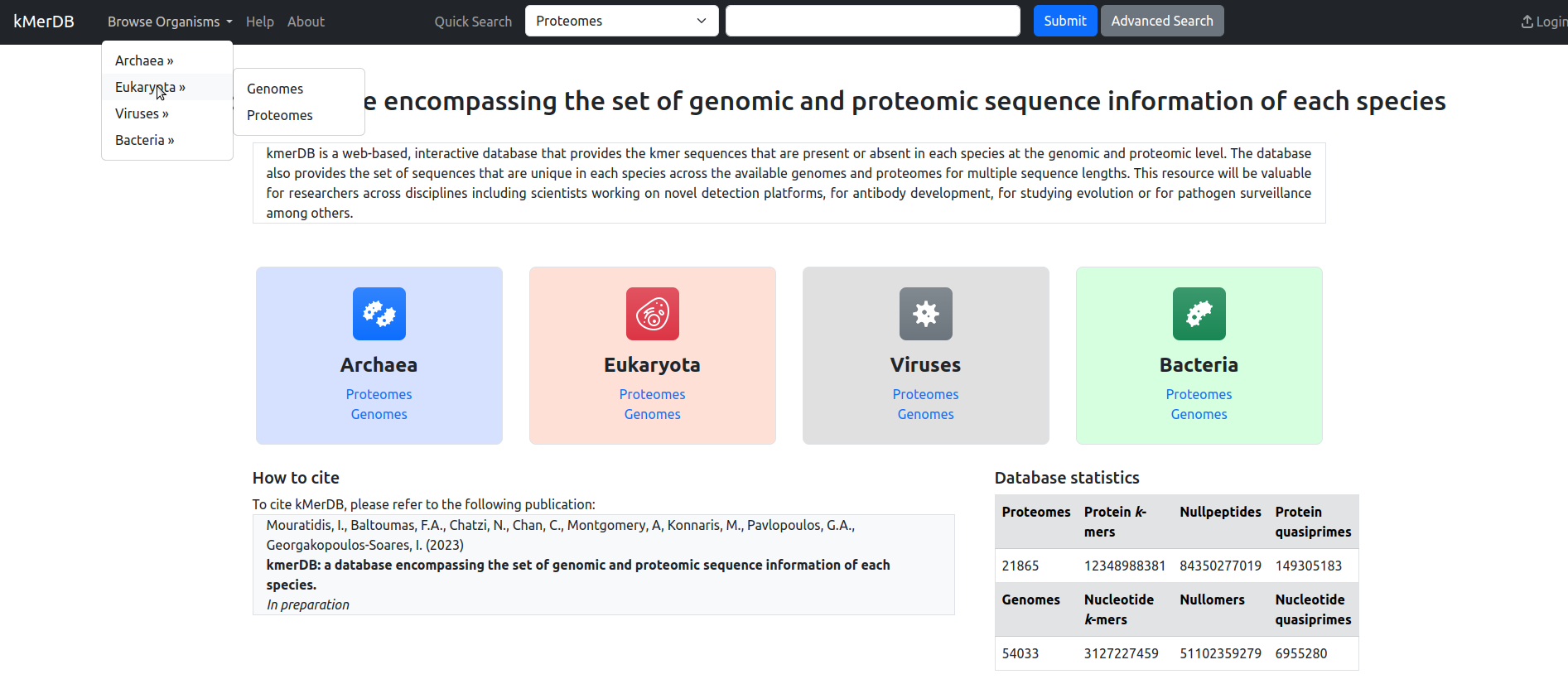
Fig. 1 The kmerDB Home page.
kmerDB enables the browsing of genomes and proteomes across the four major taxonomic groups, namely viruses, bacteria, archaea and eukaryotes. Each of them can be searched individually for reference genomes or proteomes, either from the top menu or through the panels of the landing page.
Browsing kmerDB
The user can browse through the reference genomes and proteomes to select individual species of interest based on their name or ID (Fig. 2).
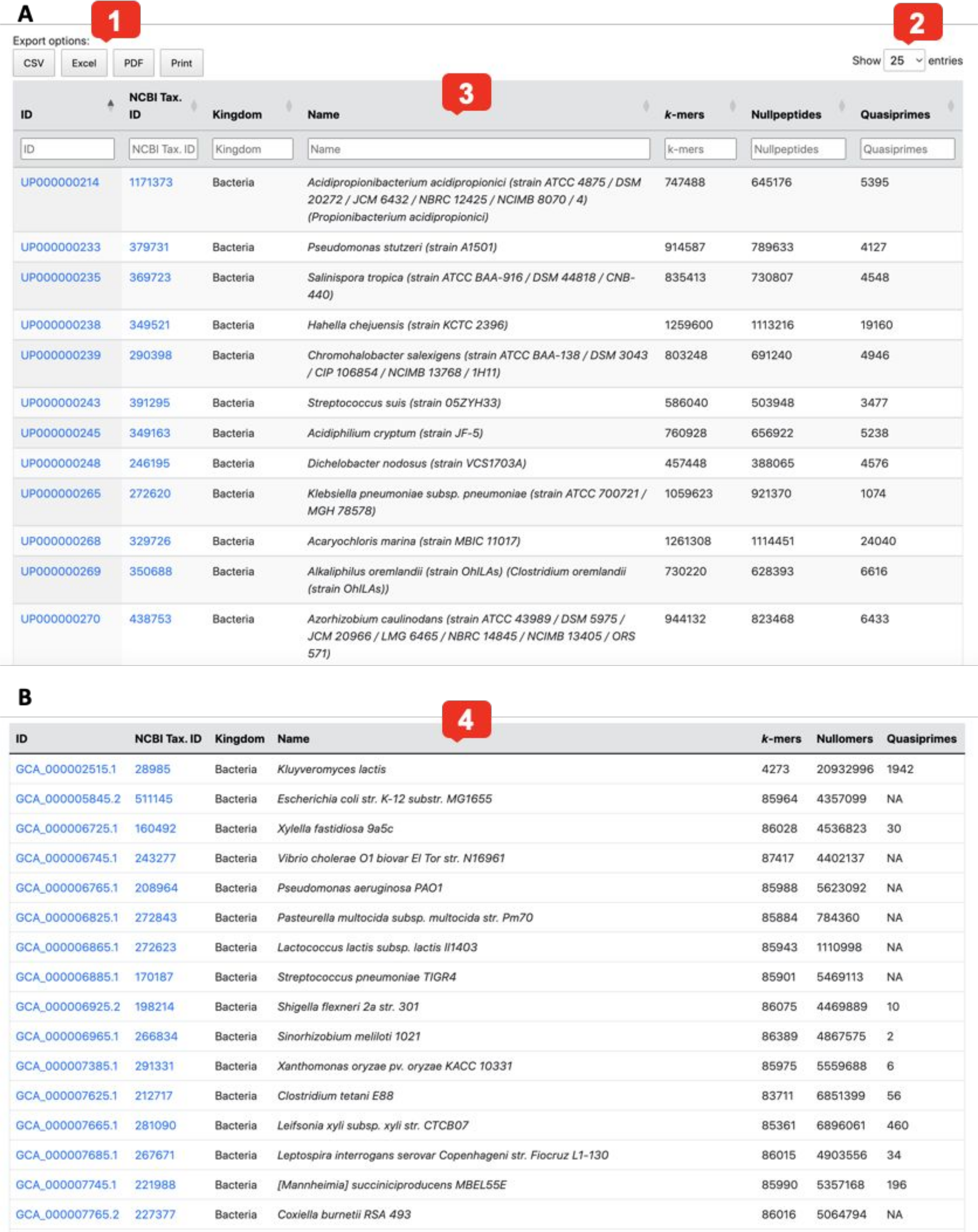
Fig. 2 Browse pages for proteomes (A) and genomes (B).
- Entries can be downloaded in various file formats by using the buttons at the top left.
- The number of entries per page can be increased or decreased by using the selector at the top right.
- Entries can be filtered using the search fields below the column headers.
- The following fields are given: Genome / Proteome ID, Kingdom, Organism name and the numbers of kmers, nullomers/nullpeptides and quasi-primes per genome/proteome.
Genome and Proteome View
For a selected proteome or genome, the user can view the associated kmers and nullomers/nullpeptides for each kmer length. Registered users can also view quasi-primes for each species (Fig. 3)
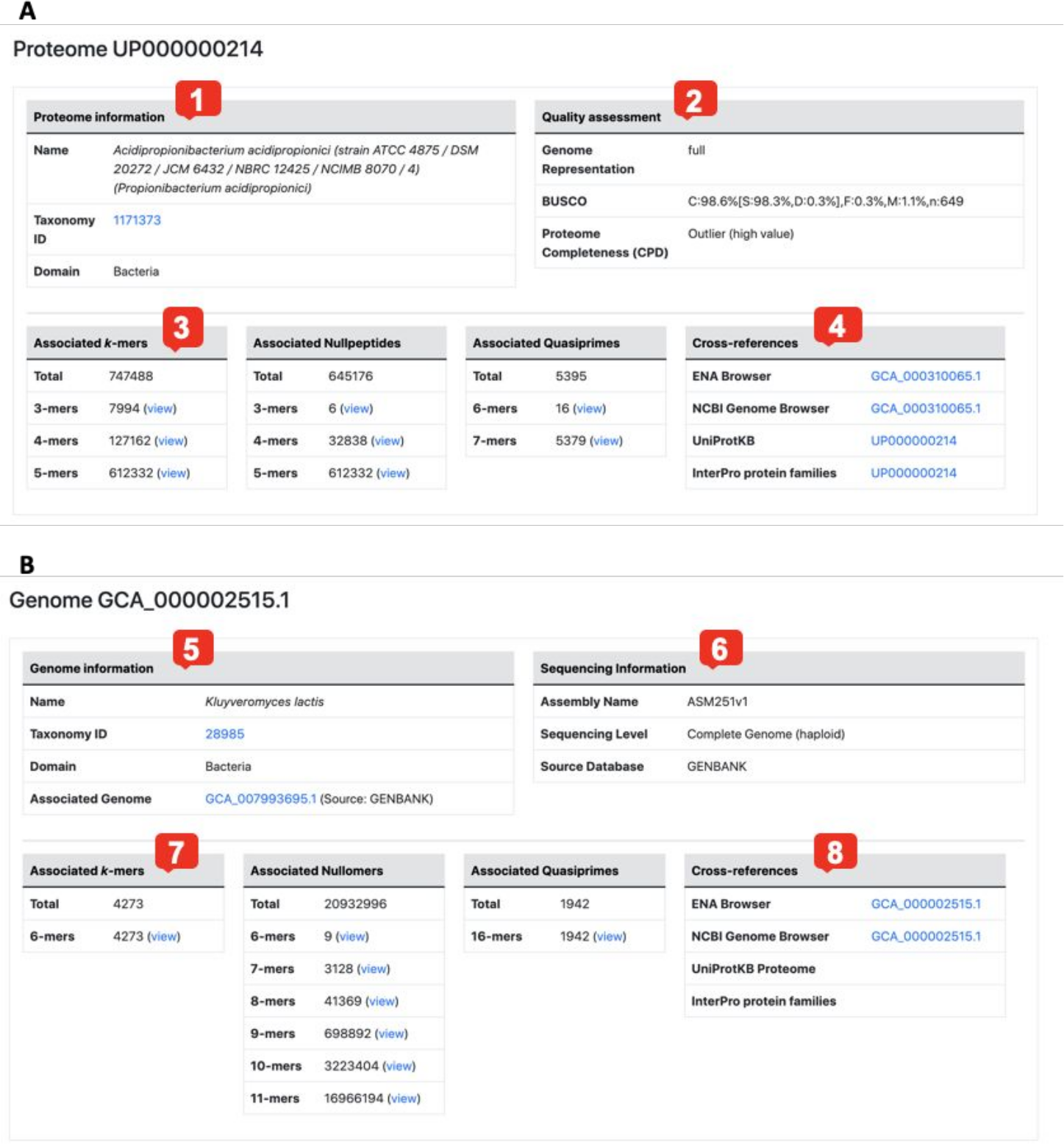
Fig. 3 Proteome and genome entry pages.
The Proteome page includes the following fields:
- Basic proteome information, including the organism name and NCBI taxonomy identifier (TaxID).
- Quality assessment: genome representation, proteome completeness level and for all cell-based (i.e. non-viral) proteomes, the BUSCO quality assessment.
- Associated kmers, nullpeptides and quasiprimes. The total counts of each n-mer length (3-mer, 4-mer etc) are given. Clicking on each link will open a page displaying the peptides associated with the proteome.
- Cross-references to major biological repositories.
Similarly, the Genome page includes the following:
- Basic genome information, including the organism name and NCBI taxonomy identifier (TaxID). In case an organism is represented by different genome assemblies, these are also listed here.
- Sequencing information, including the assembly identifier, sequencing level and source database.
- Associated kmers, nullomers and quasiprimes. The total counts of each n-mer length (6-mer, 7-mer etc) are given. Clicking on each link will open a page displaying the oligonucleotides associated with the genome.
- Cross-references to major biological repositories.
kmer visualization
The user can query the kmers, nullomers/nullpeptides, and quasiprimes of a specific genome or proteome by clicking on the respective link in the Genome/Proteome page or, alternatively, through the "Advanced Search" functionality (see next section). In all cases, the kmer/nullomer etc. visualization page is the following (Fig. 4):
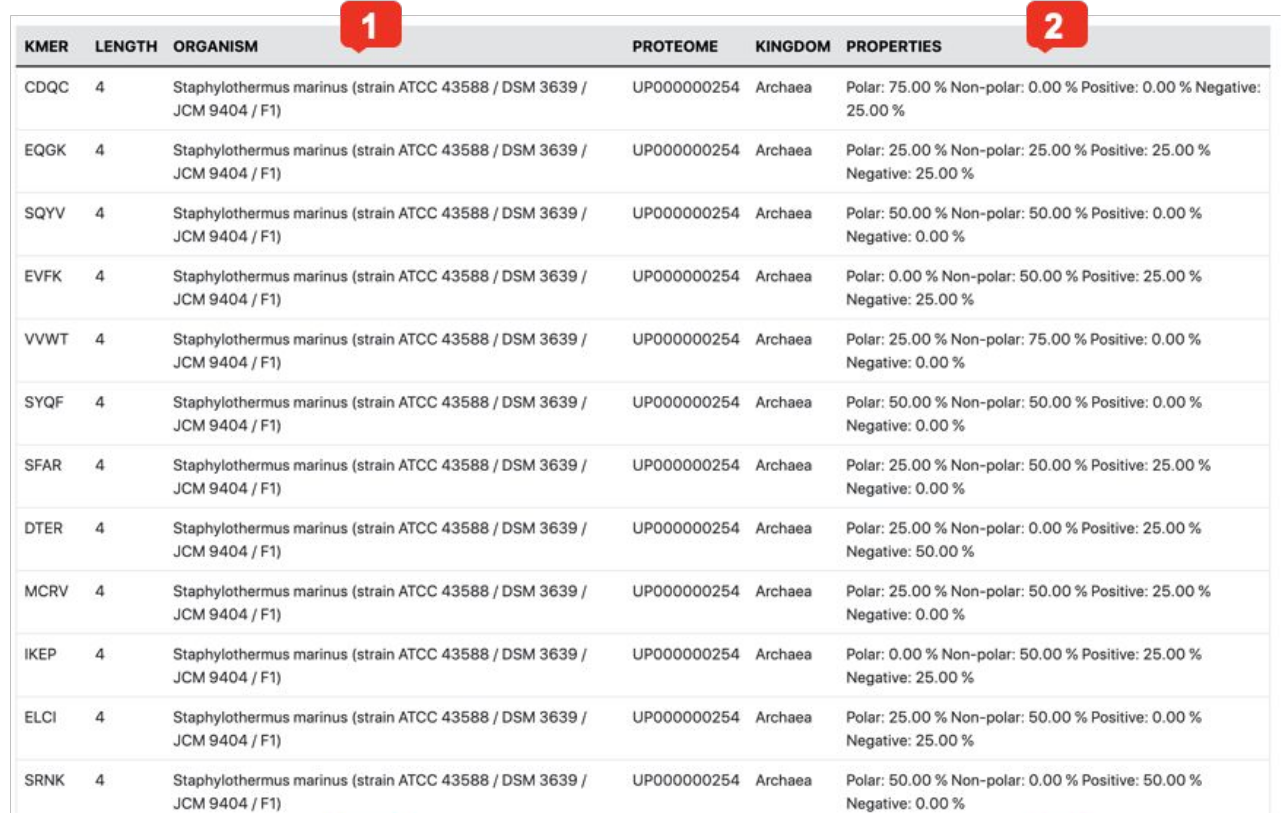
Fig. 4 kmer visualization example.
- The table contains each kmer accompanied by useful metadata, namely, its length, organism of origin and derived genome/proteome identifier.
- The Properties column contains the calculated amino acid / nucleotide properties of each kmer. For protein kmers, the physicochemical properties of the amino acids are given, while for nucleotide kmers, the percentage of each nucleotide type is presented.
Advanced Search
In addition to simple searching, filtering and browsing, the database offers advanced search capabilities, accessible through the "Advanced Search" button of the top navigation bar (Fig. 5).
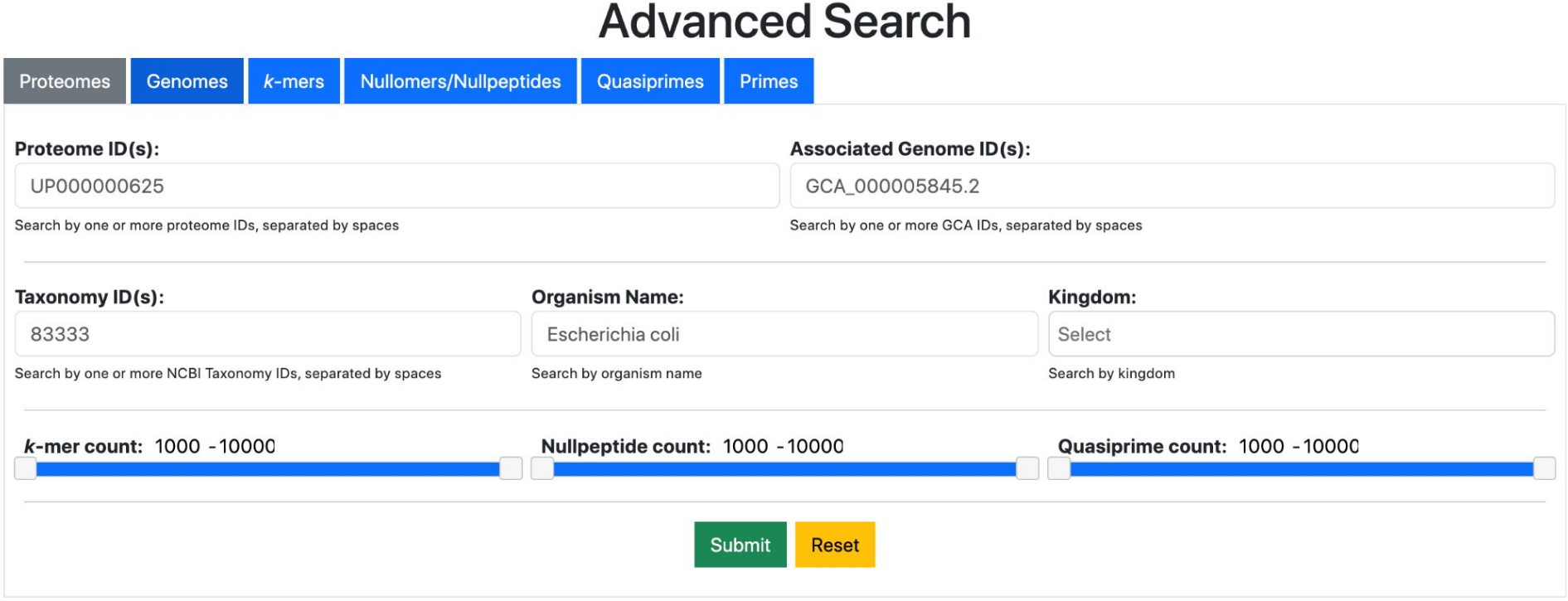
Fig. 4 The advanced search form.
The Advanced Search form enables searching for genomes and proteomes using a multitude of parameters, including identifiers, organism names/taxonomy ids. At the same time, it enables searching for all kmer types (kmers, nullomers, nullpeptides, primes and quasiprimes) with additional filters. This can be useful for combining searches, e.g. for retrieving kmers from multiple species.
Note that access to search results for quasiprimes and primes requires registration (see below).
Access to quasi-primes and primes
Currently, kmerDB offers free access to proteome/genome kmers, genome nullomers, and proteome nullpeptides. Access to proteome/genome quasiprimes and primes is restricted, and requesting for an account.
Inquiries for quasiprime/prime access should be directed at Dr. Ilias Georgakopoulos-Soares (izg5139@psu.edu) .